Benefits of Pre and Post Event sports massage for athletes
December 19, 2016
How to prevent low back pain
February 14, 2017 Doping is the act of using drugs or supplements for the purpose of enhancing performance. Many athletes in the sports and fitness community may choose to dope whether it’s for personal improvement in function and performance, to win a medal or secure a position in leagues and professional teams. These performance-enhancing drugs include anabolic steroids, growth hormones, erythropoietin and other stimulants and can be taken in the form of pills, injections or topical creams.
Doping is the act of using drugs or supplements for the purpose of enhancing performance. Many athletes in the sports and fitness community may choose to dope whether it’s for personal improvement in function and performance, to win a medal or secure a position in leagues and professional teams. These performance-enhancing drugs include anabolic steroids, growth hormones, erythropoietin and other stimulants and can be taken in the form of pills, injections or topical creams.
While these drugs can have short-term effects on the body such as increasing muscle mass, strengthen bones and tendons and increasing lung capacity; they also have adverse negative effects on health, which can be dangerous, and, in some instances, fatal. Some athletes use performance-enhancing drugs for short term but stop using it days or weeks before competitions so that they are not detected when tested.
In the UAE, the National Anti-doping Organization (NADO) is responsible for eradicating the use of prohibited drugs and enforcing anti-doping protocols to promote clean and fair sports and preserve athletic values.
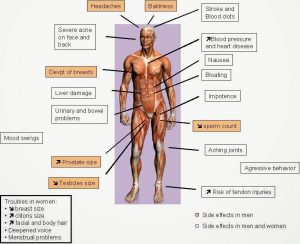
Below is of performance-enhancing drugs commonly used and their effects on the human body:
Performance-enhancing effect:
Increases muscle mass (hypertrophy) and strength
Adverse effects:
- Higher risk of tendon injuries (tendinitis, rupture)
- Skin breakout such as acne
- Liver damage
- Stunted growth and changes in puberty in children
- Development of breast tissue in men while cessation of breast development in women
- Baldness, impotence, decreased sperm production, prostate gland enlargement and shrinking of testicles in men
- Deeper voice, increased body hair, irregular menstrual cycles in women
- Increased aggressive behavior and sexual drive.
Growth Hormones (human growth hormones, insulin, erythropoietin, adrenocorticotrophin):
Performance-enhancing effect:
- Increase muscle mass and improve strength and endurance
- Erythropoietin increase production of red blood cell and hemoglobin, improving oxygen delivery to muscles
Adverse effects:
- Joint pain and muscle weakness
- High blood pressure
- Anemia
- Stroke
- Problems in thyroid gland
- Pulmonary embolism
- Blood cancers
- Human growth hormone (hGH) can cause severe headaches, heart failure, diabetes, arthritis, acromegaly (enlarged hand, feet, and face)
Beta-2 agonists
Performance-enhancing effect:
- Dilation of airways and improving lung capacity
- Used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma (found in inhalers)
Adverse effects:
- Palpitations
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Muscle cramps
- Tremors
- Increased heart rate
- Nervousness
Stimulants (such as caffeine, amphetamines, ephedrine in cold remedies)
Performance-enhancing effect:
- Improve focus and alertness by stimulating central nervous system
- Improve endurance and reduce fatigue
Adverse effects:
- Insomnia
- Anxiety
- Dehydration
- Palpitations
- High blood pressure and heart rate
- Increases risk of stroke and heart attack
- Weight loss
- Nervousness
Glucocorticosteroids
- Joint laxity and weakening of muscle, tendon, ligament
- Decreased growth in young individuals
- Loss of muscle mass
Athletes and non-athletes should think twice before using performance-enhancing drugs and should be aware of their negative effects on their bodies. Doping is prohibited by most sports organizations. Therefore, athletes competing in national or international sports events should be particularly aware of their use of medications and supplements as some may include performance-enhancing agents which are prohibited and, if detected during testing procedures, may be banned from participating in competitions.
Nermine.